Central Machine Works Announces Green Collar Beer Is Now Carbon Negative

All 3,151 pours of Green Collar beer at the CMW taproom are carbon negative and benefit the Save Our Springs Alliance.
In November 2022, Central Machine Works (CMW) Brewery in East Austin brewed the Green Collar Beer, a west coast style IPA dry hopped with Strata, Lorien, and Chinook hops from Indie Hop farms located in Oregon. The Green Collar flavor profile is somewhat juicy with notes of stone fruit and cannabis. The alcohol by volume (abv) is 6.2%, with a medium body and a light-to-style bitterness. A new technique called “mash hopping” was employed, utilizing 44 pounds of Idaho 7 American Noble Hops in the mashing process.
Beyond the flavor complexities and new techniques, CMW brewed the Green Collar to have a positive impact on the Austin community and our planet, with proceeds going to the Save Our Springs Alliance. To further the impact of Green Collar, CMW partnered with CarbonBetter to quantify the carbon footprint of the brew and offset the emissions to ensure every glass of Green Collar poured is carbon-negative.
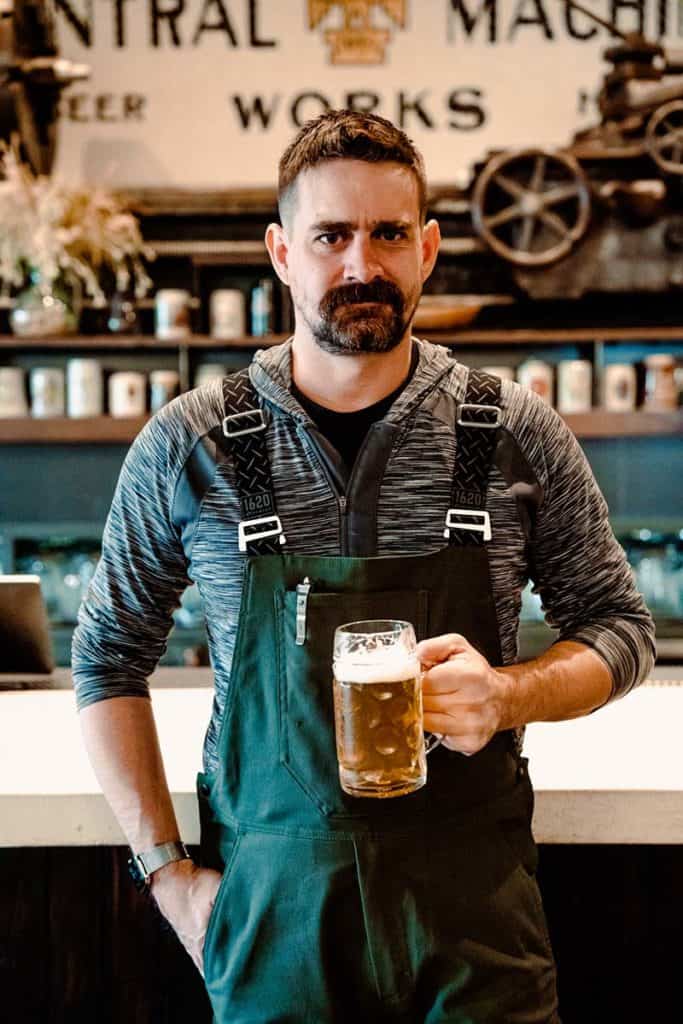



Central Machine Works’ head brewer, Scott Rynbrandt, and the Green Collar Beer.
Calculating the Emissions Footprint
To make the Green Collar Beer carbon-negative, we needed to ensure the emissions minus reductions equal less than zero. To do this, we followed these steps:
- Calculate Scope 1 emissions from natural gas consumption and Scope 2 emissions from electricity consumption.
- Calculate Scope 3 emissions based on the transport of ingredients to the brewery and offtake of spent grains to a local farmer.
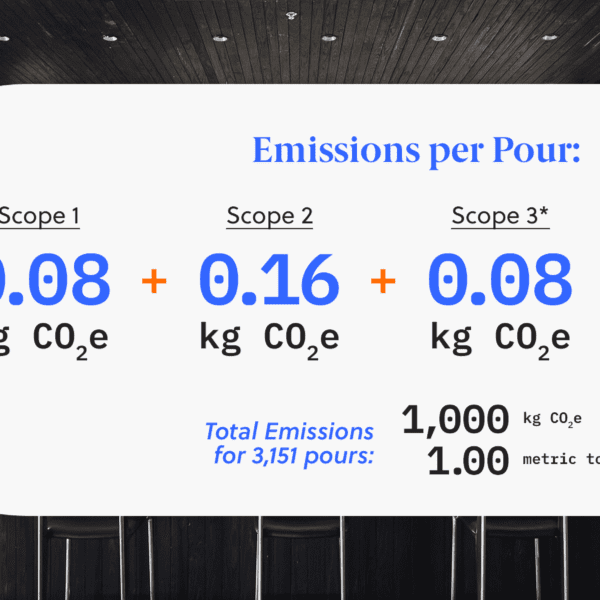
- Add Scope 1, 2, and 3 emission amounts to determine the Green Collar total carbon emissions in kilograms (kg) of carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2e) and emissions per pour.
- Offset the full emissions for all 3,151 pours of Green Collar poured at the CMW tap room by purchasing carbon credits.
About CMW’s Scope 1, 2, and 3 Emissions
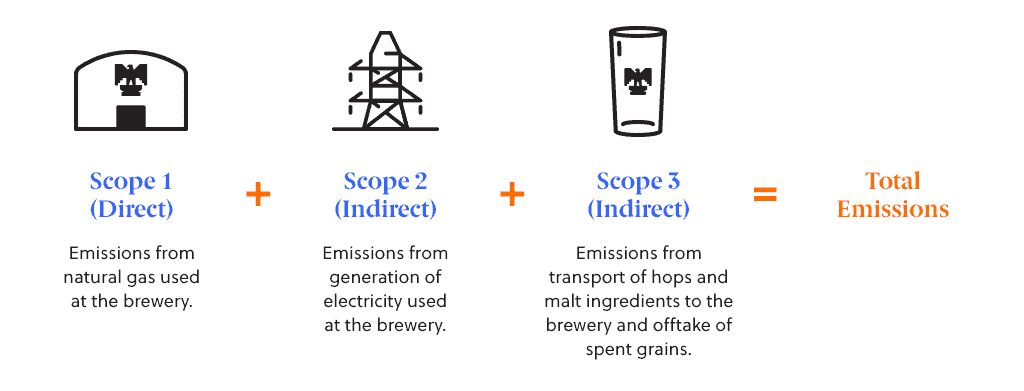
Carbon emissions for the Green Collar brew were estimated as follows:
- For Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions, the facility-wide emissions were quantified utilizing a month of utility data and normalized with the production rate of Green Collar as a percentage of the November production rate.
- Scope 3 emissions were calculated for the transport of hops and malt ingredients to the brewery and the transport of spent grains by a local farmer.
- Per pour emissions were determined by dividing total emissions for the Green Collar brew by the 3,151 pours brewed. Note, a standard pour equals 14.5 ounces.
Emissions per Pour and Total Emissions for 3,151 Pours
* transport of ingredients and spent grains only
To put these emissions into perspective, according to the EPA’s Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Equivalencies Calculator, one metric ton of GHG emissions is equal to the amount of emissions produced by:

Every Sip is Carbon Negative
To go carbon-negative with the Green Collar brew, CMW purchased carbon offset credits in the amount of two metric tons of CO2e to negate 200% of the CO2e emitted from brewing this beer. CMW has plans to evaluate opportunities to optimize energy efficiency at the brewery, and carbon credits are a tool to help mitigate harder-to-abate emissions.
Selected Carbon Offset Projects
To reach 200% carbon-negative for this release, CMW wanted to invest in meaningful projects with valuable co-benefits. CMW chose the following carbon offset projects to ensure that each sip of this charity beer would have a positive environmental impact.

Project 1: Planting Mangroves in Myanmar
SEA OF CHANGE | MYANMAR | 1 METRIC TON CO2
Given the water demands of producing beer, selecting a carbon credit with water co-benefits was important for the Green Collar project. This blue carbon project restores forests with 6 million mangrove trees planted. Only 16% of the original mangrove forest remains on the Myanmar coastline. The project reduces ~184,006 tonnes of carbon per year while simultaneously providing job opportunities to women, including leadership opportunities. The mangrove restoration efforts also maintain biodiversity while reducing the risk of seashore erosion and protecting vulnerable coastal areas against tsunamis.
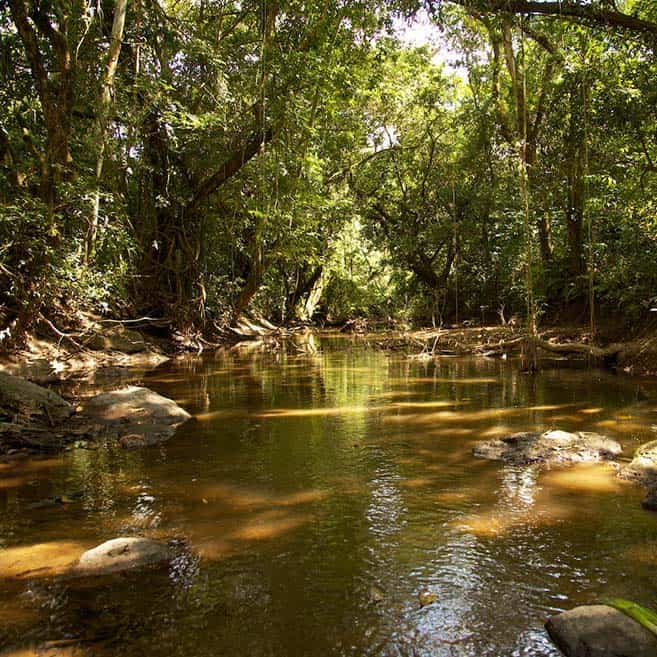

Project 2: Supporting Reforestation and Biodiversity
THE NICAFOREST HIGH IMPACT REFORESTATION PROGRAM | NICARAGUA | 1 METRIC CO2
Nature-based solutions are an important tool for sequestering carbon, so CMW also invested in the Nicaforest Program, which has planted approximately 360,000 trees to date across four farms that were previously deforested land. There is an agroforestry component to the project as the program developed a system for landless people to grow food crops in between the tree rows to improve food security in the region—more than 70 tons were harvested during the Pilot Program. The project also prioritizes watershed protection, preventing harvest from within 100 meters of rivers and creeks.
Water Impacts of the Green Collar Brew
Brewing beer is water intensive, and with proceeds from the Green Collar Brew going to the Save Our Springs Alliance, it was top of mind for CMW to consider the water impacts, inclusive of ingredient sourcing. Utilizing the World Resources Institute’s (WRI) Aqueduct tool, CMW assessed that 96% of the raw ingredients for the Green Collar Brew were sourced from Low or Low-Medium water stress regions. During the brewing process, 760 gallons of reverse osmosis water were consumed (0.24 gallons per pour), and 255 gallons were discharged as wastewater (0.08 gallons per pour). Outside of the brewing process, CMW has taken steps to minimize water consumption for irrigation by installing rain catchment at the brewery.
Waste Impacts of the Green Collar Brew
After the production of Green Collar and all other beers produced at the brewery, CMW demonstrated its commitment to participating in the circular economy by donating spent grains to a local farmer (only 4 miles away) to minimize waste and ensure reuse. The farmer utilizes the spent grains as pig feed. For Green Collar, 1,000 pounds of spent grains became pig food.
Emissions Calculation Details
Production Rate
The facility's total production rate in November 2022 was 7,440 gallons which included 357 gallons of Green Collar. Green Collar represented 4.8% of total production in November 2022. The 357 gallons of Green Collar is equal to 3,151 pours. For Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions, the Green Collar percentage of total production was applied to the representative November emissions to estimate Green Collar emissions.
Scope 1
Billing data from Texas Gas Services from the period of the start of production on October 6 through November 3, 2022 was utilized to determine the natural gas consumption for the CMW brewery representative of November operations. To estimate total emissions in CO2e, emission factors from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) were applied. Note: Natural gas consumption conservatively includes usage from the facility’s pizza oven in addition to the emissions sources applicable to brewing, including boiler and process heat.
Scope 2
CMW procures energy from Austin Energy, a City of Austin utility; utility bills from October 17 to November 15, 2022 were utilized to determine CMW’s total electricity consumption as representative of November operations and include facility-wide operations beyond the brewing process, such as the taproom. CMW applied location-based emission factors from the regional Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) grid from EPA’s eGRID database to calculate facility-wide electricity emissions.
Scope 3
CMW sourced ingredients from Germany via North Carolina and Houston as well as from Oregon and Washington. Carbon emissions associated with the transport of the ingredients were quantified utilizing the transport distances and EPA emission factors for cargo ships and trucks, as well as the weight of the ingredients procured. For emissions associated with the offtake of spent grains, the EPA emission factor for light-duty trucks and the vehicle miles traveled were utilized.
Note, Scope 3 emissions for the limited release exclude emissions from the production of raw ingredients.

About the Author
Pankaj Tanwar is Managing Director of Climate Services at CarbonBetter. He has experience leading Fortune 100 companies through their sustainability journeys, including sustainability driven growth in the food industry. Pankaj holds an MBA from Northwestern University’s Kellogg School of Management and a BTech in Mechanical Engineering from the Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur.
Are you ready to go carbon-negative?
CarbonBetter can help! CarbonBetter is a privately held firm specializing in sustainability and decarbonization services, clean energy and carbon offset project consulting, and energy logistics. We're a creative and diverse team tackling the complex climate challenges that are changing our world by helping organizations transition to a net-zero future—accelerating the societal shifts that will save our planet. We're proud to be the largest certified minority-owned business in Austin, Texas. Learn more at www.carbonbetter.com/about/.
CarbonBetter helps organizations of all sizes measure, reduce, report, and offset their emissions, and tell stories about their sustainability journey.
Telling stories about sustainability efforts helps other organizations take action that will then, in turn, inspire others—it's never too early or late to start.