Raura Hydro Electric Power Project


Certified Offset Portfolios
Buying high-quality carbon offsets has never been easier. Explore CBCO Portfolio 22-1 and get instant access to fully vetted carbon offsets.
CBCO 22-1 Project Feature: Raura Hydro Electric Power Project
Carbon offsets from the Raura Hydro Electric Power Project in India are included in CarbonBetter Certified Offset (CBCO) Portfolio 22-1, and this post shares details about the project. Click here to read other stories about projects in CBCO. Portfolio 22-1. CBCO Portfolios allow purchasers to participate in a variety of carbon offset projects in one simple transaction, rather than managing lengthy and complex request for proposal (RFP) processes in an attempt to source high-quality carbon credits from multiple projects. Learn more about the Raura Hydro Electric Power Project below and contact us to purchase from Portfolio 22-1 or learn more about custom carbon offset sourcing options to meet specific criteria.
Raura Hydro Carbon Offsets Are Included in CBCO 22-1
CarbonBetter Certified Offset Portfolios allow you to participate in a variety of projects, geographies, and technologies in one simple transaction rather than navigating a lengthy and complex RFP process with multiple organizations.
Learn More About CBCO 22-1About Carbon Offsets
Carbon offset projects allow individuals, governments, and companies to reduce their carbon footprint by investing in climate-friendly projects located around the world through the purchase and retirement of carbon offsets issued by those projects. Not all carbon offset projects are created equal, but the carbon offset market is booming as more companies make commitments to sustainability and work towards net-zero.
A carbon credit is a financial instrument that represents ownership of one metric ton of carbon dioxide equivalent that can be transferred, traded, sold, and ultimately retired. This credit represents an emission reduction or avoidance of one metric ton of carbon dioxide (CO2) or another greenhouse gas (GHG) in CO2 equivalent (CO2e), and carbon emissions are “offset” once the carbon credit is retired. In 2020 alone, companies bought more than 93 million carbon credits. By 2030, the combined voluntary and mandatory carbon credit market could add up to $100 billion, a huge increase from $300 million in 2018. Purchasing carbon credits is how companies invest in carbon offset projects to reduce their carbon footprint.
Organizations will often invest in carbon offset projects to offset their emissions because it’s cheaper for them than reducing their own carbon emissions. We encourage organizations to reduce what they can and then offset the harder-to-abate emissions. The amount of emissions avoidance or sequestration that a carbon offset project can deliver is verified by the issuing carbon offset program, and carbon offset credits are then issued that entities can purchase.
Using Carbon Offset Credits to Reach Sustainability Goals
Companies make voluntary and/or mandatory sustainability commitments, depending on whether or not they are a regulated entity that’s required to participate in a carbon trading scheme. Regardless of the type of commitment, carbon offsets help companies become low-carbon or meet net-zero goals. Corporate climate commitments typically address both direct and indirect carbon emissions, so buying carbon offset credits in combination with carbon reduction can be a smart strategy for decarbonization.
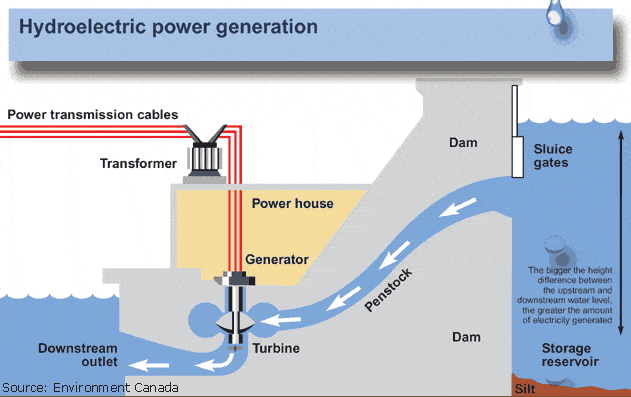
Image courtesy of USGS.gov
About the MW Raura Hydro Project by DLI Power Project
CBCO 22-1 contains carbon offset credits from the MW Raura Hydro Project by DLI Power in addition to offsets from three other high-quality projects. The MW Raura Hydro Project provides clean energy to northern India by harnessing renewable electricity from a small, run-of-river hydroelectric power plant, minimizing both the overall environmental impact of the dam and the amount of fossil fuels needed to supply the regional grid.
India relies heavily on carbon-intensive, coal-fired power plants that contribute to climate change. Fortunately, India has the potential to tap into many renewable energy projects, including hydropower. In 2019, India overtook Japan as the fifth largest hydropower producer by capacity with installations generating 50,071 MW. In 2016, the Government of India estimated that 7,135 potential power generation sites could generate 21,135.37 MW of power from small and mini hydro projects as determined by the Alternate Hydro Energy Centre (AHEC) of IIT Roorkee.
“The MW Raura Hydro Project provides clean energy to northern India by harnessing renewable electricity from a small, run-of-river hydroelectric power plant, minimizing both the overall environmental impact of the dam and the amount of fossil fuels needed to supply the regional grid.”
Nicole Sullivan, former Director of Climate Services at CarbonBetter
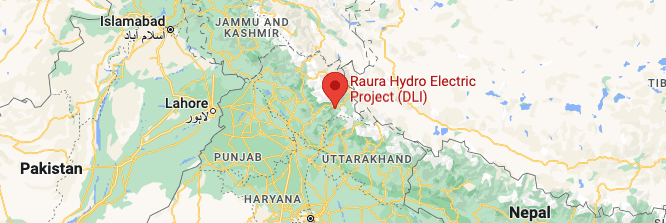
Project Location
The MW Raura Hydro Project is located in the Kinnaur District of Himachal Pradesh (HP). The State of HP alone has an estimated hydro potential of 2,736 MW out of which 24,000 MW has been assessed and 20,912 MW has been allotted under various sectors. This carbon offset project is developed and owned by DLI Power India Private Limited. DLI Power is part of DLZ Corporation, one of the foremost engineering and water resource companies in the Midwestern United States.
Project Registry
The MW Raura Hydropower Project is registered on Verra’s Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) with a 2021 vintage.
UN Sustainable Development Goals
The UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) that this project directly and indirectly satisfies are SDG 7 (affordable and clean energy); SDG 6 (clean water and sanitation); SDG 9 (industry, innovation, and infrastructure); and SDG 13 (climate action). Some additional SDGs that this project can satisfy through co-benefits are SDG 1 (end poverty); SDG 3 (good health and well-being); SDG 4 (quality education); SDG 8 (decent work and economic growth); SDG 11 (sustainable cities and communities); and SDG 12 (responsible consumption and production).
Further, VCS identified these specific SDGs:
- Social well-being: SDG indicators 1.1, 3, 3.8, 8.6, and 9.1;
- Environmental well-being: SDG indicators 7.2, and 13;
- Technological well-being: SDG indicators 7.2, and 13;
- Economic well-being: SDG indicators 1.1, 3, 8.6, and 7.2; and
- Other associated well-being: SDG indicators 4.3, 8.8, and 3.
Project Technology
This project generates clean energy by utilizing renewable natural resources that generate electricity through a hydropower dam. This particular carbon offset project uses a “run-of-the-river” type of dam with a turbine that has an electricity-generating capacity of 12 MW. The technology involves three Pelton-type horizontal axis turbines, each with a capacity of 4 MW installed and commissioned. The hydropower facility converts the potential energy available in the water flow to mechanical energy using its hydro turbines, which turn the generators and create electricity. The renewable electricity generated is exported to the grid via Himachal Pradesh State Electricity Board (HPSEB) under a Power Purchase Agreement (PPA).
According to VCS, this project will offset anthropogenic GHG emissions by reducing approximately 61,495 MWh/year of electricity at the grid—an estimated emissions reduction of approximately 56,726 tCO2e per year. The total estimated reduction of GHG emissions for the chosen 10-year renewable crediting period will be 5,67,262 tCO2e.
Project Co-Benefits
This project also has several important co-benefits. The hydroelectric dam provides renewable electricity for nearby communities and contributes to conservation projects that protect habitats and watersheds. This project also produces zero carbon emissions or harmful air and water pollutants like SOx, NOx, and SPM associated with coal-fired power plants.
Additionally, it provides water management, climate mitigation and adaptation services, and energy storage. The dam generates additional income for the community through the direct sale of electricity, and it helped improve local infrastructure by adding a road and a water pipeline while providing direct and indirect jobs from construction and ongoing maintenance. As a renewable energy project, it also promotes investment in technology for small hydropower plants as well as reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
The project developer also invested in programs to support the nearby community, including constructing a playground, offering health clinics and education programs, the distribution of free food, and pandemic relief support for poor and vulnerable populations.
Carbon offset credits from the MW Raura Hydro Project by DLI Power are included in CBCO 22-1. Interested in purchasing portfolio units, or sourcing specific credits that meet your needs? Contact CarbonBetter today to request more information about this particular project as well as our CarbonBetter Certified Offset (CBCO) Portfolios.